Linux users are searching for a way via the command prompt to modify the file/directory permissions Chmod modifies each document's rights by mode, in which the mode specifies the privileges to be updated You may designate a mode with octal numerical or letters In this article, Linux Chmod Command Tutorial for Beginners is explainedIn Linux systems, "chmod" command is used to determine the access rights of users to filesIt allows us to change the access permissions of the files we specify The exact equivalent of chmod is change mode When we examine the example below;Extra chmod command options Verbose Changes Silent Default Recursive PreserveRoot Reference File Setuid Setgid Sticky Bit Use the octal CHMOD Command chmod R 700 folder_name OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command chmod R arwx,grwx,orwx folder_name Chmod Permissions for chmod 700 Chmod owner Owner can read;

Linux Command In Hindi Part 10 Youtube
Chmod command in linux in hindi
Chmod command in linux in hindi-Numeric Method # The syntax of the chmod command when using numeric method has the following formatChown and Chmod commands for managing file permissions in Linux system Time:5 chown Usage chown options owner group file Or chown options — Reference = reference file Change the owner and / or group of each file When using the — referenbce parameter, change the owner and group of the file to be the same as the specified reference file



Pazeidimas Diskriminacinis Riaumoti Ubuntu Wc Yenanchen Com
Chmod command in Linux is used to change or assign permissions on files and directories In Linux / Unix systems, accessibility to files and directories is determined by file ownership and permissions In a previous article, we looked at how to manage file & directory ownership using the chown command In this tutorial, we look at the chmodUse the chown command to change file owner and group information we run the chmod command command to change file access permissions such as read, write, and access This page explains how to use chmod and chown command on Linux or Unixlike systemsThe command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or Directory The Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or Directory Also Read Linux Tutorial for Beginners && Git Tutorial for Beginners
Now, let us see how chmod command can be used to change the access mode of a file Example 1 Let's change the assgn1_clientc permission so that the owner cannot write(w) in the file but can only read it BEFORE rwrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc COMMAND chmod u=r assgn1_clientc AFTER rrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc BeforeThe chmod command stands for change mode and it's used to limit access to resources It's a same as using your mouse to rightclick a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and defining who can access the resource the chmod command is the way to do it on the command lineH ow do I use chmod and chown command under Linux / Unix operating systems?
Actually, in early Unix days, permissions were called mode of access This is why this particular command was named chmod chmod command has the following syntax chmod option mode file Before you see how to use chmod, you should know its optionsH ow do I use chmod and chown command under Linux / Unix operating systems?Chmod 755 Only owner can write, read and execute for everyone This next command will set the following permission on file rwxrxrx Only the owner will be allowed to write to the file Owner, group members and everyone else will have read and execute permission chmod 755 /path/to/file



Linux Basic Commands In Hindi Part 1 By Leloknowledge



Chmod 777 Chmod 755
Chmod is a Linux command that will let you "set permissions" (aka, assign who can read/write/execute) on a fileNumeric mode The format of a numberic mode is 'augo' A numeric mode is from one to four octal digits (07), derived by adding up the bits with values 4, 2, and 1 Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros The first digit selects the set user ID (4) and set group ID (2) and sticky (1) attributes The second digit selects permissionsChmod command in linux chmod कमांड का मतलब होता है change mode



9 Termux Youtube Channel Ideas Youtube Channel Computer Knowledge



Linux Umask Tutorial Hindi Youtube
लिनक्स की कमांड (Linux Commands)bc Command Chmod command s dca notes in hindi Linux commands in hindi pgdca notes in hindi pgdca operating system notes in hindi 1 Comment Click here to post a comment Ritu gupta says March 12, 17 at 528 amThe following terminal commands can help you get a basic idea of how the chmod 777 command works on Linux chmod 777 filename sudo chmod 777 /var/www/ sudo chmod R 777 /var/www/ In the picture above, you can see that the output starts with the dr syntax, and it has the wxr syntaxes along with it, which means that the target path is a directory and it has the write, execute, and read permissionIt is common to use the basic chmod command to change the permission of a single file However, you may need to modify the permission recursively for all files within a directory In such cases, the chmod recursive option (R or recursive) sets the permission for a directory (and the files it contains) The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is



Hindi Install Kali Linux 19 Without Termux Root Anlinux One Click By Nitish Kumhar



Kill Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Chmod ur ABCtxt chmod uw ABCtxt chmod ux ABCtxt where, ur is to disallow a user to read the contents of the object uw is to disallow a user to make modifications to the object ux disallows a user to execute the object Similarly, to add permission for a group – chmod gr ABCtxt chmod gw ABCtxt chmod gx ABCtxtThe chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode The chown command stands for "change owner" is used to change the owner of a given file or folderChmod stands for change mode This command is used for changing the mode of access But wait!



Move Between Directories Complete Linux Course Class 3 Urdu Hindi 21 Benisnous



Pazeidimas Diskriminacinis Riaumoti Ubuntu Wc Yenanchen Com
Use the chown command to change file owner and group information we run the chmod command command to change file access permissions such as read, write, and access This page explains how to use chmod and chown command on Linux or Unixlike systemsExtra chmod command options Verbose Changes Silent Default Recursive PreserveRoot Reference File Setuid Setgid Sticky Bit Use the octal CHMOD Command chmod R 700 folder_name OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command chmod R arwx,grwx,orwx folder_name Chmod Permissions for chmod 700 Chmod owner Owner can read;{Updated} This page explains how to use chmod and chown command on Linux or Unixlike systems The post How To Use chmod and chown Command in Linux appeared first on nixCraft This post first appeared on NixCraft — Linux Tips, Hacks, Tutorials, And Ide , please read the originial post here



Linux Basic Commands In Hindi Part 1 By Leloknowledge



Use Scp Command In Linux To Copy Files Securely Over Ssh Protocol
The command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or Directory The Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or Directory Also Read Linux Tutorial for Beginners && Git Tutorial for BeginnersChmod commands in Hindi chmod शब्द का अर्थ "Change mode" है। यह कमांड फाइल या फोल्डर डायरेक्टरी को read, write और execute करने का एक्सेस अधिकार (Access Permission) बदलने के लिए उपयोग3421 The chmod command A normal consequence of applying strict file permissions, and sometimes a nuisance, is that access rights will need to be changed for all kinds of reasons We use the chmod command to do this, and eventually to chmod has become an almost acceptable English verb, meaning the changing of the access mode of a file


Termux Irc Chat Log



Ubuntu Ubuntu Operating System Booting
Chmod command in Linux is used to change or assign permissions of files and directories In Linux systems, accessibility to files and directories is specified by file ownership and permissions The chmod command in Linux stands for change mode is utilized to manage file and directory permissions$ chmod ax sampletxt Allow read permission to everyone $ chmod ar sampletxt Make a file readable and writable by the group and others $ chmod gorw sampletxt Make a shell script executable by the user/owner $ chmod ux samplescriptsh Allow everyone to read, write, and execute the file and turn on the set groupIDHow to Use chmod Command Let's say we want to change Linux file permissions from rwxrwrw to rwxr–r– Simply enter this line chmod 744 file name By executing this command, the owner can read, write, and execute the file ( rwx ) However, group and others are only allowed to read ( r– )



Setting Up Emby Server On Linux Zap



Linux Basic Commands In Hindi Part 1 By Leloknowledge
Linux Chmod Command Tutorial for Beginners – Linux Hint Most of the fresh users to Linux are searching for a way via the command prompt to modify the file/directory permissions Those users would be pleased to know that there is a command – dubbed or chmod, eg change mode – that help you do this quicklyU stands for userIs it not meant for changing the permission?



How To Install Android Studio In Ubuntu 04 Install Android Studio Linux Ubuntu Android Golectures Online Lectures



How To Remove Directory In Linux By Command And Gui Guide For Beginners
Chmod Linux commands in Hindi chmod का पूरा नाम "Change mode" है। यह कमांड का उपयोग फाइल या फोल्डर डायरेक्टरी को read, write और execute करने का एक्सेस अधिकार (Access Permission) बदलने के लिए किया जाता है।We can sort it as a user, group and other from left to right, which comes in 3 blocks after the first characterThe chmod command modifies the permission mode of objects in the system It is one of the most used and important commands in the set of Linux security commands A plus () symbol adds a permission, and a minus () symbol removes a permission You can read chmod ur as "user plus read," as it gives the user read permission



Linux Pocket Guide In Hindi
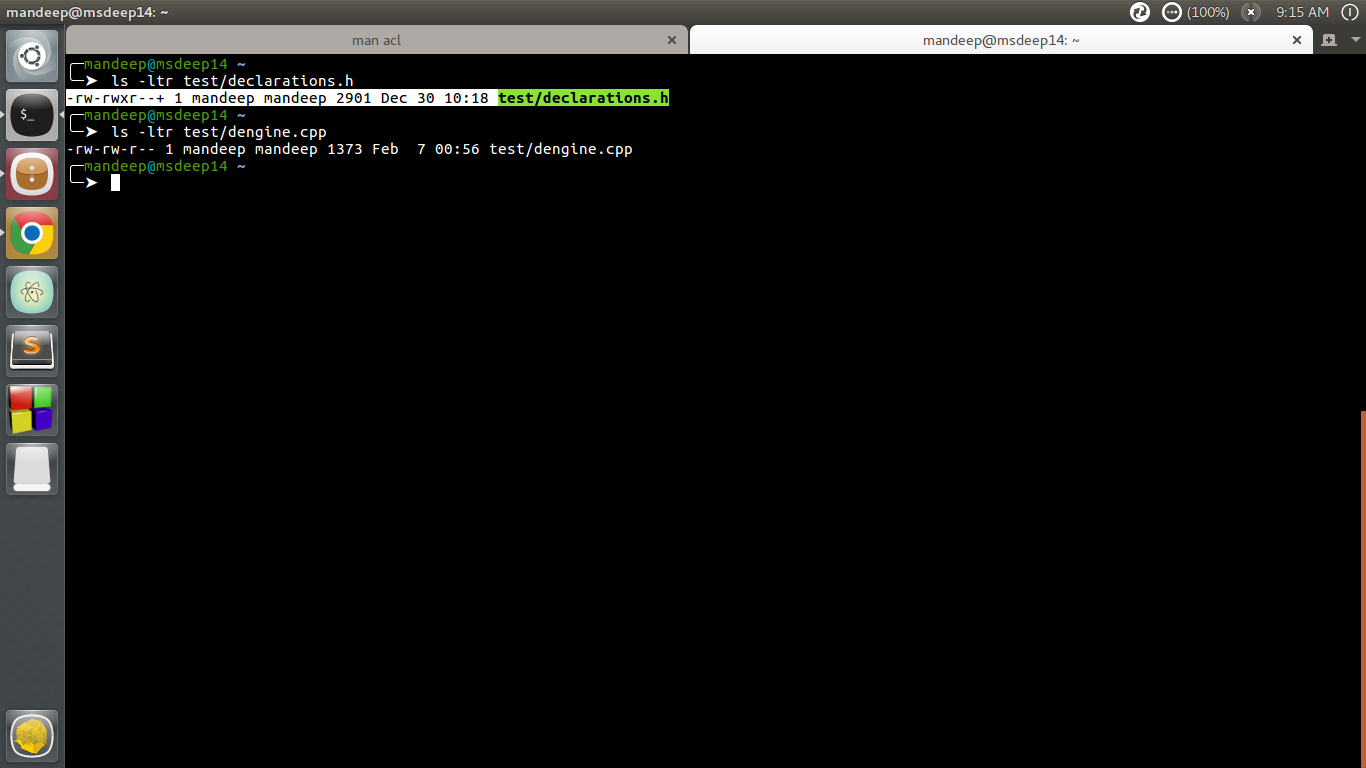


Access Control Lists Acl In Linux Geeksforgeeks
The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls commandThe chmod command A normal consequence of applying strict file permissions, and sometimes a nuisance, is that access rights will need to be changed for all kinds of reasons We use the chmod command to do this, and eventually to chmod has become an almost acceptable English verb, meaning the changing of the access mode of a fileAdd a sticky bit to a given directory chmod ot dirname;



How To Customize Rhel 8 0 Linux Terminal Urdu Hindi


Extending Hyperledger Fabric Network Adding A New Peer By Abdul Wahab Medium
Types of permissions which we will be changing using chmod command In linux terminal, to see all the permissions to different files, type ls l command which lists the files in the working directory in long format The figure below shows an example to use ls l and its output Let us take a look at above figureHow to use the chmod command in Linux First, open terminal Then use the cd command to go to the directory where the file you want edit is Now use the following command to see the permission granted to the file Ls –l filename Now you just need to use the attributes explained above Use the following example to execute the chmod command in Linux Chmod {user}{add or remove permission}{permoission}Others can read only" chmod R 755 myfiles Recursively (R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755 User can read, write, and execute;



Linux Command Line Tutorial Shell Basics



09 Linux File Permissions Commands With Examples Hindi Urdu Youtube
Description This command is used for change of permission for the user of the file The permission for owner of the file has changed from "rw" to "rwx" chmod ux /home/zivi/cat Linux File Permission – Add Permission for Owner of Files Description use of " u " with " x " is optionalThe chmod and chown commands are powerful and most popular command line tool that can be used to control access to files in Linuxbased operating systems The chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode The chown command stands for "change owner" is used to change the ownerThe chmod system call cannot change their permissions This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointedto file



Up Board Solutions For Class 10 Computer Science Chapter 5 Linux Operating System



Update Virtualbox On Ubuntu Without Losing Existing Data Uk2blogger Vulnerability Tutorial Data
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;$ chmod gx appsh Change File Mode For Other Others is special group which covers all users in a Linux system We can enable the execution right of the all users in a file with o like below $ chmod ox appsh Change File Mode For All In some cases we can see the x without a definitionChmod ux scriptsh As you'd have guessed, 'ux' says grant () the owner/current user (u) execute (x) access to the file Similarly, for group, you can use 'g' and for others you can use 'o' Please note that whenever you want to grant/revoke a common set of permissions to/from all, you can use 'a' instead of 'ugo'



5 Best ह क ग कम ड क ज नक र Hacking Commands In Hindi



How To Configure Samba Step By Step Samba Configuration In Ubuntu 16 4 Linuxtopic
Using chmod Command Chmod कमांड का सामान्य रूप निम्नलिखित रूप लेता है $ chmod OPTIONS MODE FILE Use Symbolic method in chmod CommandGroup members and other users can read and execute, but cannot writeChmod R or *page Numerical Shorthand Another way to use chmod is to provide the permissions you wish to give to the owner, group, and others as a threedigit number The leftmost digit represents the permissions for the owner
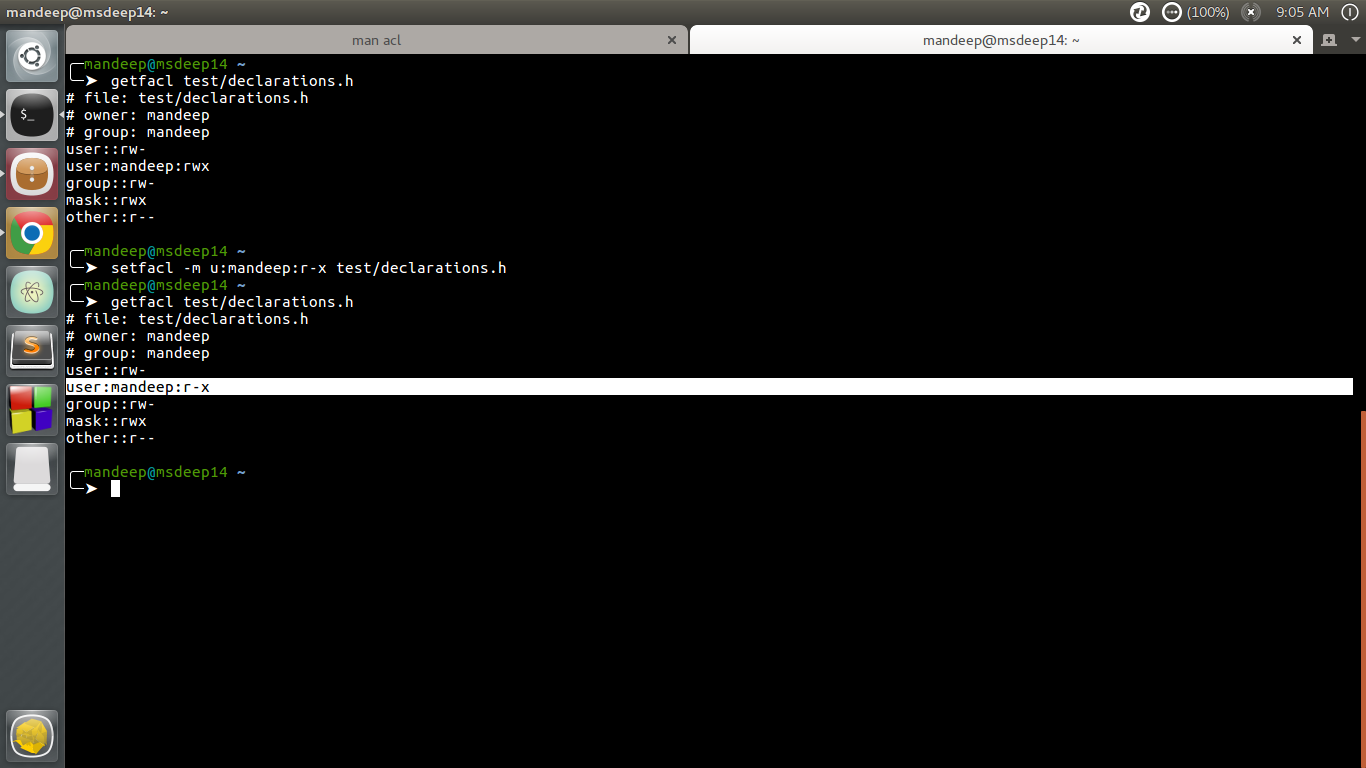


Access Control Lists Acl In Linux Geeksforgeeks



About Kaali Linux 17
Group can read only;Examples chmod 644 filehtm Set the permissions of filehtm to "owner can read and write;This video covers the chmod command in depth and everything you want to know about change modeBoth Octal and symbolic modes



Linux Commands For Beginners 13 Viewing Logs Digital Ocean Promo Code



Termux Irc Chat Log
{Updated} This page explains how to use chmod and chown command on Linux or Unixlike systems The post How To Use chmod and chown Command in Linux appeared first on nixCraft This post first appeared on NixCraft — Linux Tips, Hacks, Tutorials, And Ide , please read the originial post hereYou can change the permissions given to a file using the chmod command chmod can be used in 2 ways The first is using symbolic arguments, the second is using numeric arguments Let's start with symbols first, which is more intuitive You type chmod followed by a space, and a letter a stands for all;How to use the chmod command in Linux First, open terminal Then use the cd command to go to the directory where the file you want edit is Now use the following command to see the permission granted to the file Ls –l filename Now you just need to use the attributes explained above Use the following example to execute the chmod command in Linux Chmod {user}{add or remove permission}{permoission}



Learn How To Use The Command Line For Linux And Mac Includes A Free Printable Containing The Commands Browse Linux Learn Computer Coding Computer Programming



Linux Admin Basics Part 5
We can sort it as a user, group and other from left to right, which comes in 3 blocks after the first characterChown and Chmod commands for managing file permissions in Linux system Time:5 chown Usage chown options owner group file Or chown options — Reference = reference file Change the owner and / or group of each file When using the — referenbce parameter, change the owner and group of the file to be the same as the specified reference fileUsing "Chmod x" Command on Linux and Unix with Examples In Linux systems, " chmod " command is used to determine the access rights of users to files It allows us to change the access permissions of the files we specify The exact equivalent of chmod is change mode When we examine the example below;



How To Install Kali Linux On Android Without Root Full Version Android Operating System Linux



How To Install Kali Linux On Android Without Root Full Version
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the R, (recursive) option The general syntax to recursively change the file's permissions is as follows chmod R MODE DIRECTORYAdd the file's owner permissions to the permissions that the members of the file's group have chmod gu filename;



Linker Computing Wikipedia



How To Use Google Translate From Commandline In Linux Ostechnix



コレクション Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi



Linux Basic Commands In Hindi Part 1 By Leloknowledge



11 Useful Commands For Kali Linux And Parrot Security Os Beginners Tutorials Android Windows And Linux Based Tips Tutorial



Splunk
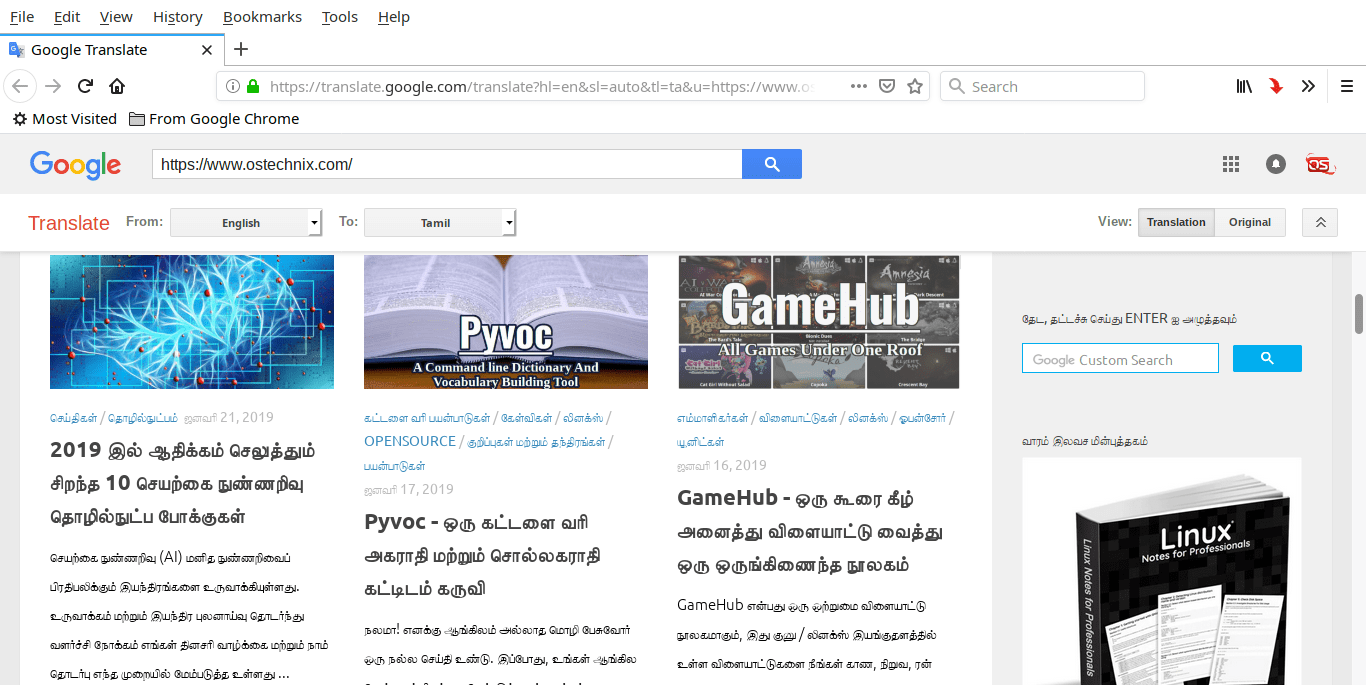


How To Use Google Translate From Commandline In Linux Ostechnix



Computer Linux Command All Comptetive Exams In Hindi By Study Hub



Linux Command Chmod In Hindi Youtube



52 Uk2blogger Ideas In 21 Online Earning Linux Google Blogger


Linux Laravel Questions



Pazeidimas Diskriminacinis Riaumoti Ubuntu Wc Yenanchen Com


最も好ましい Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi さもがた
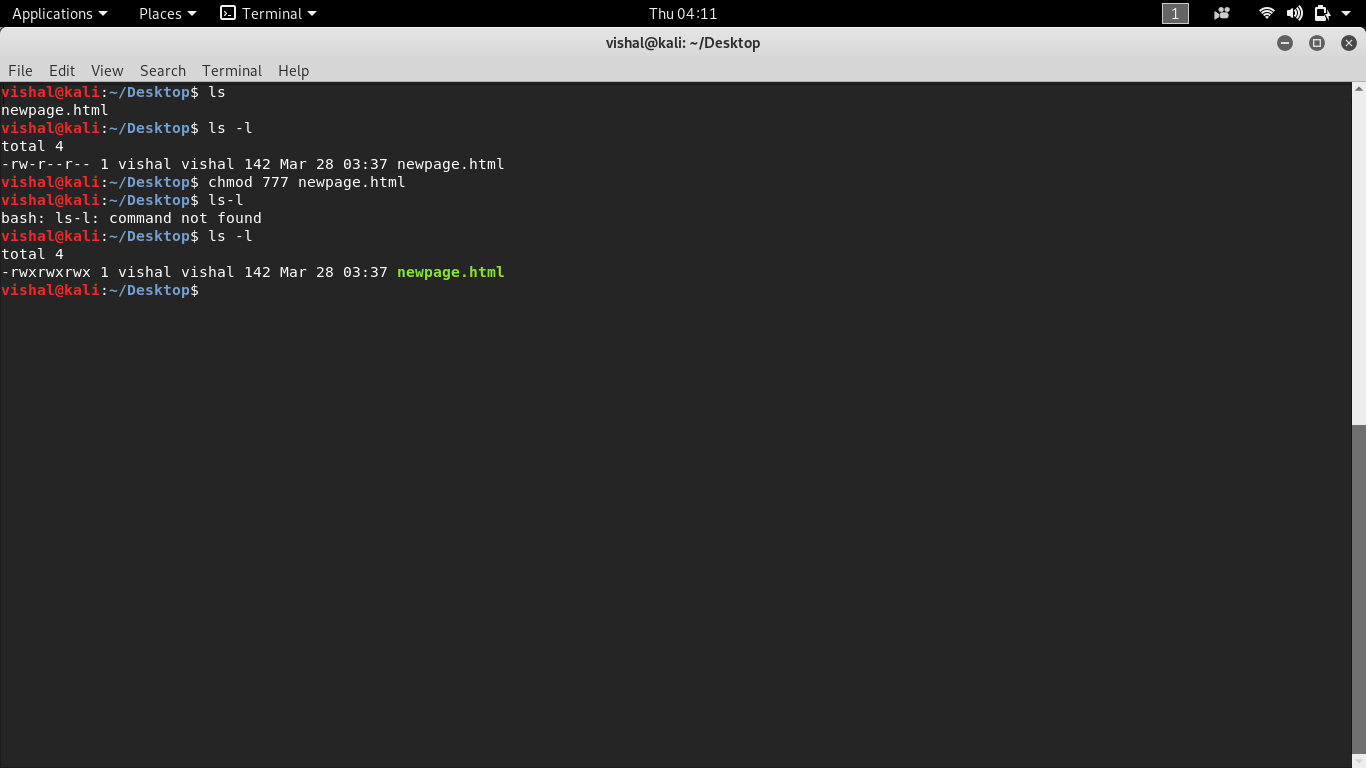


Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example



Pazeidimas Diskriminacinis Riaumoti Ubuntu Wc Yenanchen Com



Linux Command In Hindi Part 10 Youtube



Linux Command In Hindi Part 9 Youtube



Linuxcommand



How To Install Chrome In Kali Linux Digital Ocean Promo Code



12 File Permission In Linux User Group All Other User Permission In Hindi Youtube


最も好ましい Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi さもがた



Building An Android Command Line Application Using The Ndk Build Tools Digit



Linux Tutorials In Hindi Chown Change Ownership Command In Linux Hindi Tutorial Youtube



08 Unix Linux Shell File Directories Permission Chmod Command Youtube
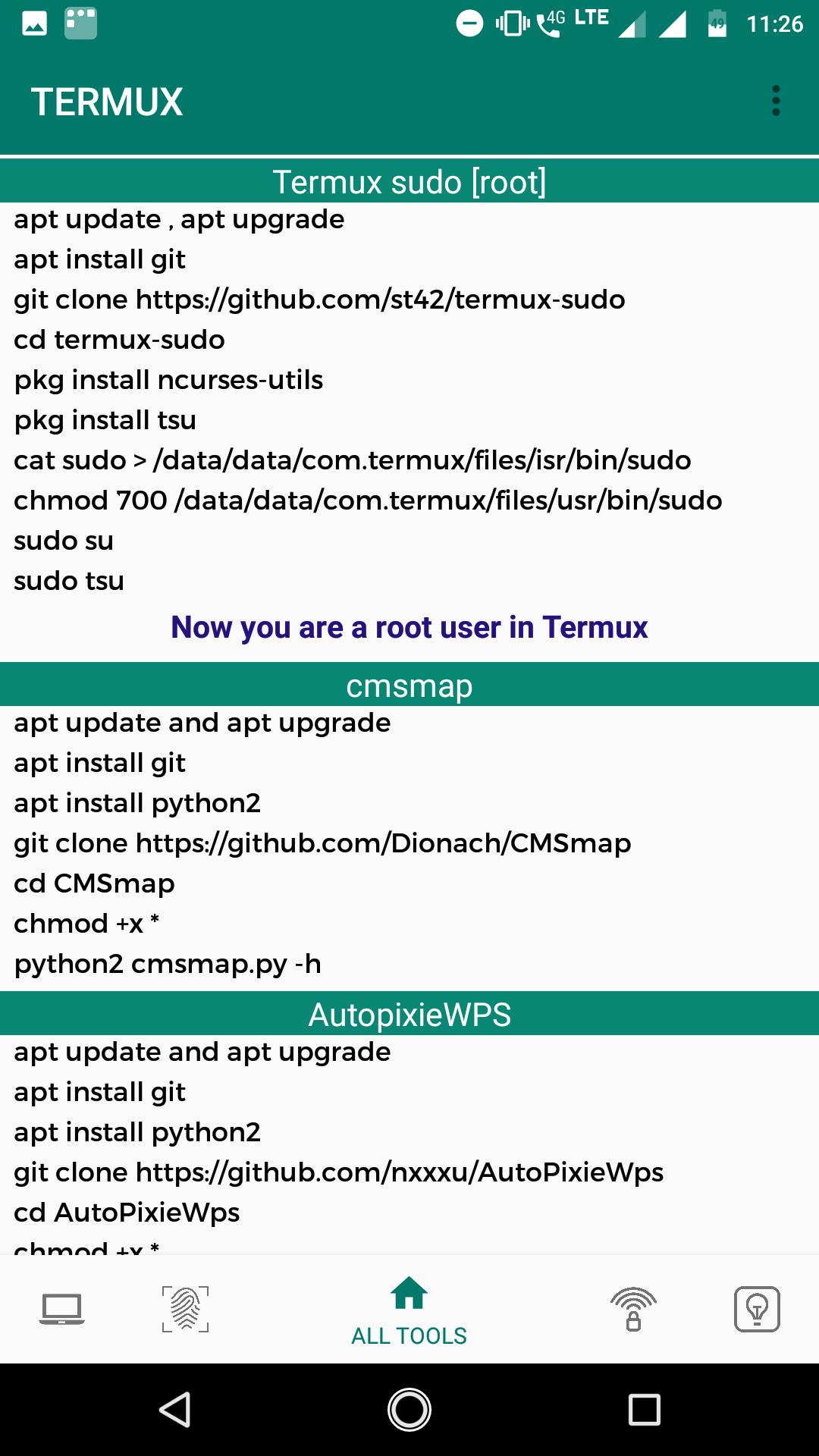


Commands And Tools For Termux For Android Apk Download



Download How To Use Date Command In Hd Mp4 3gp Codedfilm


Linux Tutorial Linux Command Line Tutorial Linux Installation Edureka



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change



Pin By Stanislav Jirak On Cybersecurity Computer Knowledge Computer Projects File Server


最も好ましい Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi さもがた



Touch Command In Unix By A Onetutors



Linuxcommand



Complete List Of Useful Ubuntu Linux Commands For Programmers



How To Use Chmod 777 Command In Linux Explained How To Use Chmod Command Hindi Tutorial Youtube


Nethunter Rootless Kali Linux Documentation



Pin On aaa



Question How To List All Files In A Directory Linux Os Today



Sun Solaris Unix Commands And Scripts Home Harman Induced Info



15 Group And Owner Permission In Centos 7 Rhel In Hindi Youtube



最も好ましい Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi さもがた



T Bomb For Bombing In Termux No Root By Noob Hackers Golectures Online Lectures


Getting Hardware Information From Linux To Help Forum Staff Page 2 Linux Org


Build Your Own Oracle Infrastructure Part 7 Build Oracle Rac Servers Nudais Consulting Llc



How To Install Virtual Box Guest Addition On Kali Linux Simple Method Summary Networks



Hindi Linux What Is Chmod And How To Use Chmod In Linux Youtube



570 Linux Unix Ideas Linux Unix Linux Operating System



How To Get Root Permission For Installing Application On Kali Linux Explained Hindi Golectures Online Lectures



Best 30 Basic Linux Commands In Hindi For Beginners Usehindi Com



52 Uk2blogger Ideas In 21 Online Earning Linux Google Blogger



Pazeidimas Diskriminacinis Riaumoti Ubuntu Wc Yenanchen Com



How To Create New Users Groups In Linux Cloud Network



Pazeidimas Diskriminacinis Riaumoti Ubuntu Wc Yenanchen Com



2 Linux Notes Booting Superuser



Linux Command Line Interface Chmod Command In Hindi Youtube



Computer Linux Command All Comptetive Exams In Hindi By Study Hub



Introduction To Linux By Dds Dds Issuu



Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



Chmod 777 Chmod 755



Linux Command Line Tutorial Learn The Bash Command Line Linux Terminal Tutorial



How Tp Track Someone Location In Termux With Ip Address Hindi Benisnous



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿